Git
- Git is a version control system.
- You can think of it as a time machine for code.
- A commit is like a checkpoint in your code.
- With Git, you can track changes, go back to older versions, and collaborate with others.
Repository
A repository (or repo) is just a project folder tracked by Git.
It contains:
- Code
- Documentation
- History of changes
Repositories can live locally (on your machine) or remotely (e.g., GitHub).
Basic Git Commands
git status
git config --global --list
git config --global user.email "your_email@example.com"
git config --global user.name "your_name"
git initBranches
git branchLists all branches in the repo.
In a fresh repo without any commits, no branch is shown, because Git requires at least one commit to recognize a branch.
git add .
git commit -m "initial commit"After your first commit, you’ll see the master (or main) branch.
Flow & File Stages
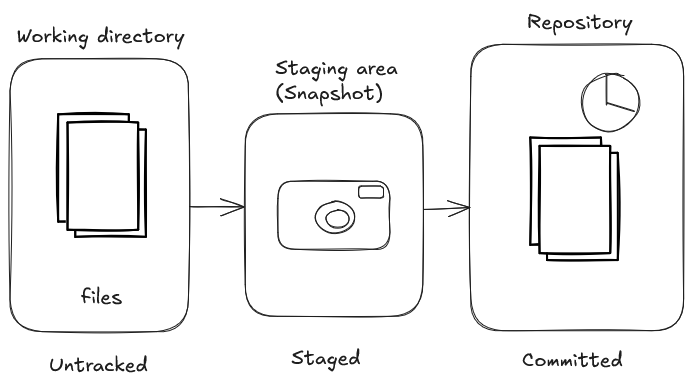
Git Stages
- Untracked → New files not yet tracked by Git.
- Modified → Tracked files with changes.
- HEAD → The latest commit on the current branch.
When you create a new branch, it starts from the HEAD of the current branch.
Logs
git log --oneline
git reflogUsed to check details, history, and metadata of commits.
Ignoring & Empty Folders
- Use a .gitignore file to exclude files you don’t want Git to track.
- Git doesn’t track empty folders. To force it, create a .gitkeep file inside the empty folder.
Working with Branches
git switch master
git switch -c feature_branch
git checkout -b feature_branch- If the branch doesn’t exist, Git will create it.
Merge
git mergeis used to combine branches
- Merge in Git combines two branches together, preserving their commit history.
- Merge creates an extra commit (called a merge commit) when histories diverge.
- In case of merge conflicts, you can:
1. Keep master’s changes
2. Keep the branch’s changes
3. Combine both
git merge --abortAbort a merge in progress.
Rebase
Rebasing moves the base of a branch to a different commit.
- With rebase, merges can be fast-forward (no extra merge commits).
eg to update feature branch with the latest main:
git checkout feature
git rebase mainTime Traveling with Git
git reset --hard HEAD~1
git reset --hard <commit_id>- Reset to a previous commit (using commit ID is safer).
git resetcan also unstage changes.
Cherry Picking
- When we don’t want to merge an entire branch and only need a specific change from it.
- Pick specific commits and bring them into your branch:
git cherry-pick <commit_id>
git cherry-pick <commit id1> <id2> <id3>.- You can cherry-pick multiple commits too (in order).
- If we pick commits out of order, we might run into conflicts because the later commit could rely on code that was introduced in an earlier one.
- If commits are independent, we can cherry-pick them in any order.
Stashing
- Stashing lets us save uncommitted changes in a temporary stack and come back to them later.
Stash = temporary storage for your changes.
git stash push -m "paused my development"
git stash list
git stash apply
git stash pop- If we don’t give a stash ID,
applyandpopuse the most recent stash.
Git Commands
git initInitialize the repository as a git repository.
git clone <repo-url>Clone a remote repository locally.
git remote -vShow remotes linked to the repository.
git remote add origin <url>Add a remote repository.
git statusShow the status of changes in the working directory and staging area.
git add ./git add <filename>Add files to the git repository to start tracking.
git diffShow changes between the working directory and the staging area.
git commit -m "<message>"Commit the git changes to the repository with a clear commit message.
git branchCheck how many branches of the repo there are.
git branch <branch name>Create a new branch with branch name.
git branch -m mainRename the current branch to
main.
git checkout <branch name>Switch working directory to branch name.
git merge <branch name>Merge the specified branch into the current branch.
(It does not always merge into
master; it merges into whichever branch we are currently on.)
git rebase masterIf we want the changes made in the master branch to reflect in a branch we use rebase command.
This rewrites the commit history of the branch by running its commits on top of the branch.
To ensure preservation of git history and isolation of changes a better alternative is to merge with the master branch.
git pushPush the changes to the remote repository.
git push origin mainPush the local
mainbranch to the remote.
git pull origin mainFetch and merge the latest changes from the remote
mainbranch.
git pull origin main --allow-unrelated-historiesPull changes even if local and remote histories are unrelated.
git logSee the log of all the recent commits.
git log --onelineSee only single line log for each commit.
git reflogProvides a history of branch movement, useful to find a commit if need to reset.
git resetUnstage changes that were added with
git add, without modifying the working directory.
git reset --hard <commit id>Moves HEAD pointer to given commit id and completely discards changes in the staging area and working directory after the commit id.
git reset --soft <commit id>Moves HEAD pointer to given commit id and without discarding changes in the staging area and working directory after the commit id. Used to "undo" a commit.
Resources: